Abstract
Aggressive natural killer cell leukemia (ANKL) is a rare form of natural killer (NK)-cell neoplasm with median survival of less than 2 months. Recently, the genomic mutation analysis using tumor cells reveled that the mutational profile of ANKL was similar to that of extranodal NK / T-cell lymphoma, which has relatively better prognosis than ANKL, explaining no causative mutations with a dismal prognosis. Here, using patient-derived xenograft model (PDX) mouse, we show that hepatic niche plays an important role in the ANKL biology.
We established PDX mouse by intravenously injecting ANKL cells derived from patient peripheral blood or bone marrow samples to immunocompromised mice, which enables comprehensive analysis for tumor cells as well as tumor microenvironment. In total, we obtained four PDX strains derived from different patients. Time series pathological and flowcytometric analyses revealed that the ANKL cells initially engrafted and proliferated in sinusoidal or peri-portal area of the liver. This sinusoid or peri-portal distribution of ANKL in the liver was also confirmed with the patient liver specimen.
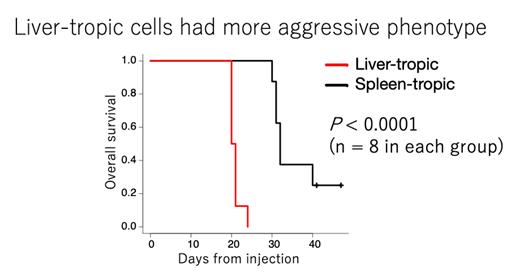
To further determine the feature of ANKL in the liver, we selected liver or spleen tropic cells by serial adaptive transfer from each organ to the next mice. The liver-tropic ANKL cells proliferated more rapidly than splenic ANKL cells, which was evident by the significantly shorter survival of PDX mice injected liver-tropic cells (Figure). We performed RNA-sequencing using liver-tropic ANKL cells, spleen-tropic ANKL cells and NK-cells derived from healthy donors. These three types of cells showed distinct populations in principal component analysis. To further clarify the interaction between ANKL and liver niche, we performed additional RNA sequencing using total liver of mouse with or without bearing leukemic cells. In the cell-cell interaction analysis, we used two computational methods, mixed-species RNA-seq (Komura, et al. BMC Genomics 2016), which can distinguish transcripts derived from human (cancer) with mouse (non-cancer niche cells), and NicheNet (Browaeys, et al. Nat Methods 2020), which is a computational algorithm to model intercellular communication by linking ligands to target genes. These two methods allowed us to investigate the interaction between liver niche ligands and ANKL receptors.
Among the listed ligand-receptor interactions, we focused on the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and its receptor, CD74 axis. While CD74 was upregulated in ANKL cells compared with normal NK cells, MIF was highly expressed in the liver mainly liver sinusoid and Kupffer cells. Although we failed to culture primary ANKL cells in vitro, ANKL cells treated with MIF showed improved viability in vitro compared with untreated cells. Deletion of CD74 on the ANKL cells using CRISPR-Cas9 system attenuated the tumor formation in the liver as well as in bone marrow and spleen of PDX mouse compared with the wild type ANKL cells. These findings highlight that the liver, non-canonical hematopoietic organ in adults, is a principal niche where the liver specific components are required for survival and proliferation of ANKL cells. MIF-CD74 axis might play an important role in the communication between ANKL and hepatic niche.
Kanda: Otsuka Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; MSD: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal